The certificate in SSL certificate management is bound to the domain name. Therefore, when purchasing a certificate, you need to select the corresponding domain name type.
After selecting the domain name type and successfully purchasing the certificate, you need to bind the corresponding domain name to the purchased certificate, that is, you need to complete the certificate audit data in the SSL certificate management. The first step in applying for a certificate is to fill in the domain name information and bind the corresponding domain name to the purchased certificate.
The SSL certificate management console will prompt you for the type of domain name you need to enter based on the certificate you purchased.
The specific description of each domain name type is shown in Table 1. For more reference content, please refer to the specific example.
Table 1: Binding domain names
|
Parameter name |
Parameter description |
|
Single domain |
Only 1 common domain name can be bound. When binding domain name, you can bind one common domain name. |
|
Multiple domain |
* Multiple domains can be bound (several domains can be bound if the number of purchased domains is several). * When applying for a certificate, you need to set one of the domain names as the "main domain name", and the other domain names as "additional domain names". You can choose according to your actual situation. For example, if the number of domain names you purchased is 3, set 1 domain name as the main domain name, and set the other 2 domain names as additional domain names. Notes: The relationship between the main domain name and the additional domain name (master-slave relationship) has no effect on the added domain name. If you purchase a combined certificate (single domain name extensive domain name), the main domain name only supports binding a single domain name.
|
|
Wildcards
|
Only one domain name can be bound. When binding a domain name, you can bind a extensive domain name with *. |
Concrete example:
1. Single domain certificate
When you purchase a single-domain certificate, only one common domain name can be bound.
Example: Your domain name is example.com
When applying for a certificate, just fill in example.com in "Binding Domain Name", as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Single domain binding domain name

2. Multi-domain certificate
When you purchase a multi-domain certificate, you can bind multiple domain names (several domains can be bound if the number of purchased domains is several).
When applying for a certificate, you need to set one of the domain names as the "main domain name", and the other domain names as "additional domain names". You can choose according to your actual situation. Additional domain names can be entered multiple times in batches. For details, please refer to Adding Additional Domain Names.
Notes:
The relationship between the main domain name and the additional domain name (master-slave relationship) has no effect on the added domain name.
If you purchase a combined certificate (single domain name extensive domain name), the main domain name only supports binding a single domain name.
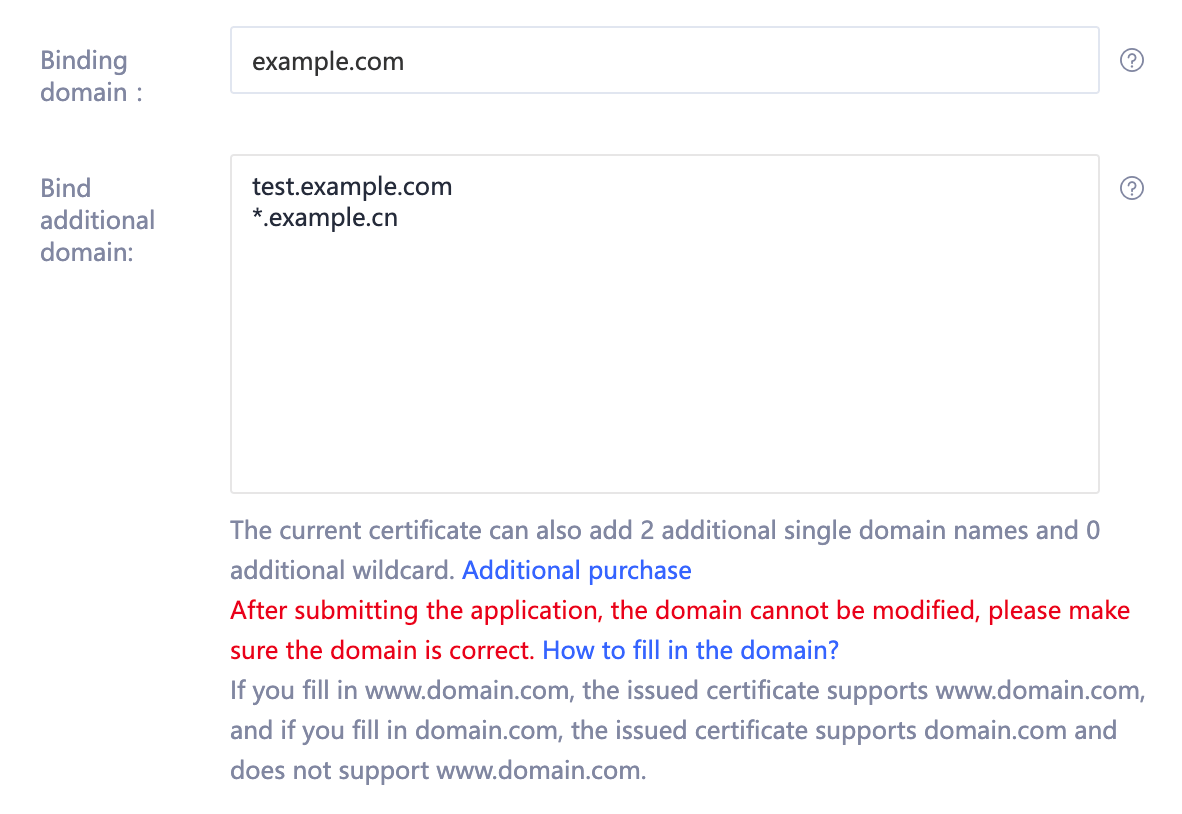
Example: If the number of purchased domains is 3 and your domains are example.com, test.example.com and *.example.cn
When applying for a certificate, fill in example.com in "binding the main domain name", and fill in test.example.com and *.example.cn in "binding additional domain name". Multiple additional domain names require newline input, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Multi-domain binding domain name
3. Wildcard domain certificate
When you purchase a wildcard domain name certificate, you can bind a generic domain name.
Example: Your domain names are test.example.com, yun.example.com, example.example.com, good.example.com, etc., all at the same level
When applying for a certificate, fill in "*.example.com" in "Binding Domain", as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: bind domain for wildcard domain



















